Apple with iOS 8 is advancing the CoreLocation API with new features designed to provide users with even more reliable, faster and precise indoor positioning in supported venues. Currently, iOS determines your location using a combination of GPS, a crowd-sourced location database of nearby Wi-Fi hotspots and the cellular triangulation technique that determines your rough location based on cell tower signal strength.
As GPS/cellular are often unavailable or perform poorly inside buildings and in underground places like parking lots, iOS 8 can resort to using a combination of iBeacon transmitters, if any, and motion data provided by your device’s accelerometer, compass and gyroscope sensors…
And if you own an A7-powered device like the iPhone 5s, iPad Air or iPad mini with Retina display, iOS 8 will entrust use the power-efficient M7 motion coprocessor with collecting data from motion sensors in a battery friendly manner, without waking up the main A7 processor.
As Apple explains in a video titled “Taking Core Location Indoors”, available on the WWDC 2014 webpage, precise indoor positioning needs participating venues to sing up to help improve indoor positioning:
iOS 8 makes it possible for an iOS app to determine its precise indoor position in supported venues. Learn best practices on how your app can take advantage of indoor positioning.
Discover how indoor positioning and iBeacon complement each other, and understand the best use cases for both technologies. As a venue, find out how you can get involved and signup to enable indoor positioning.
And, venues that do sign up can even put app shortcuts right on the Lock screen when a user is nearby, even if they don’t have the app installed on their device.
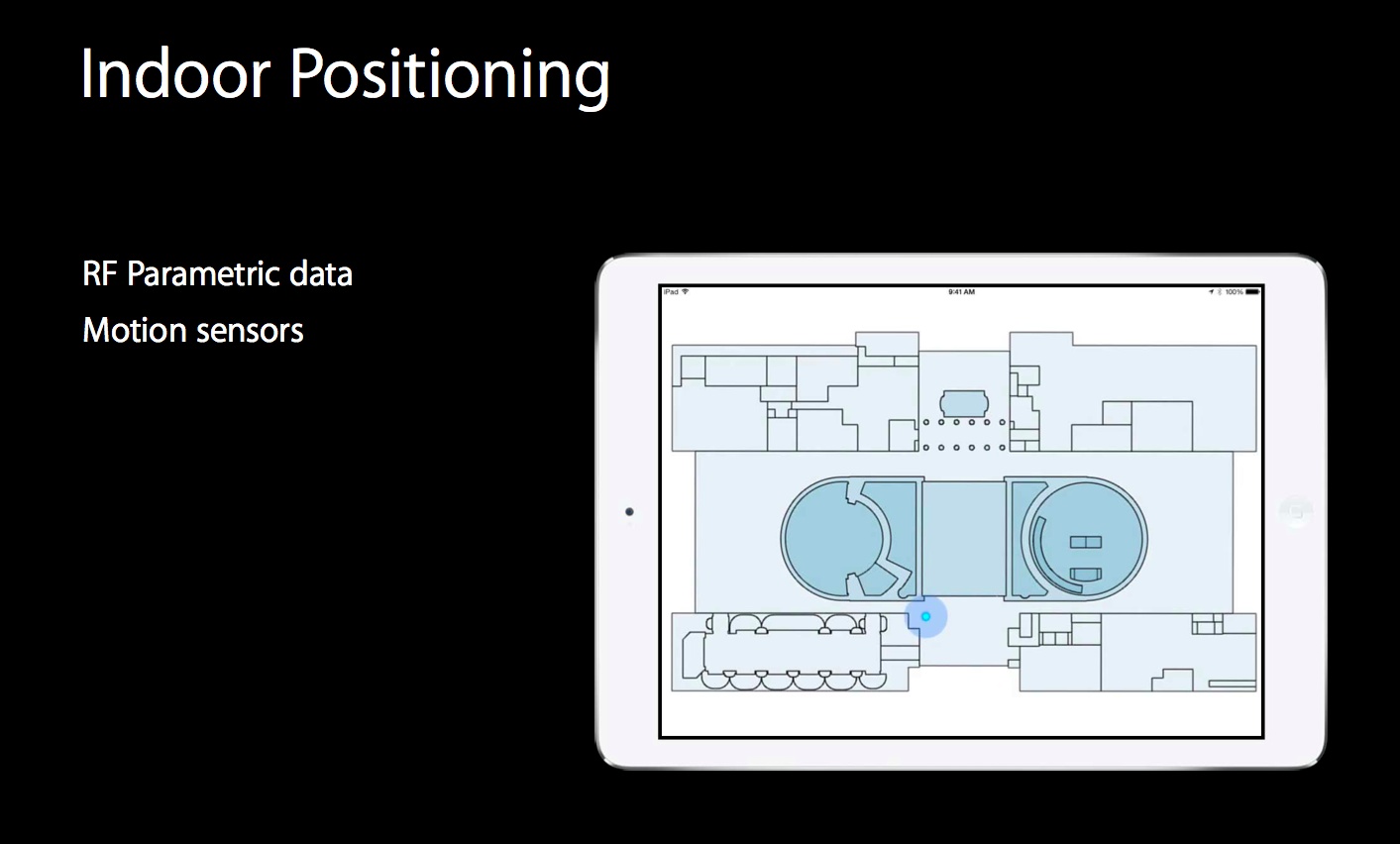
The slide deck [PDF download] reveals that iOS 8 can determine a user’s indoor position by interpreting both the data from the device’s sensors and RF parametric data provided by the participating venues, bypassing GPS altogether.
The technique requires the device to be unlocked and Wi-Fi to be enabled.
Micro-positioning enabled by this technique provides the level of accuracy needed to determine your precise location inside a venue, down to the exact floor number.
The fact in turn leads us to speculate that Apple could be working on adding detailed indoor maps to its Maps service. As a reminder, Apple last year snapped up a company called WiFi Slam to help improve indoor positioning.
Developers don’t need to do anything on their part: as long as they are using Apple’s CoreLocation API to retrieve a user’s location, the API will return a user’s precise indoor location wherever possible.
Examples include indoor navigation inside circular spaces like Apple’s upcoming iSpaceship campus and art galleries, where the system could provide relevant content based on exhibits nearby.
Apple notes that while iBeacon provides proximity information and enables push notifications for nearby devices, indoor positioning is for position and navigation.
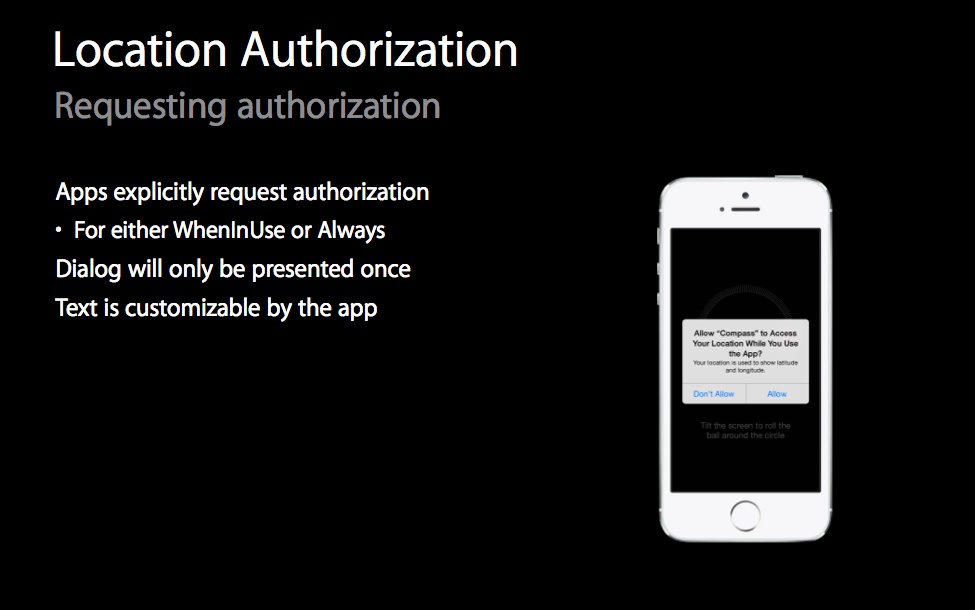
Requesting your indoor position comes with a brand new ‘When In Use’ iOS 8 prompt which essentially asks for permission to only use your location when an app is in use.
Some of the signed up venues include the Westfield San Francisco Centre and the California Academy of Sciences in San Francisco, with more to come in the coming months.