We’ve talked quite a lot about Recovery OS, an underestimated feature of OS X that makes it easier to troubleshoot your Mac even if it refuses to start up properly.
But as you’ll see for yourself in this post, Recovery OS is but one of the more than dozen different ways to start up your computer, aside from OS X’s regular startup mode. In this tutorial, we’ll list all the ways you can start up your Mac and detail each one.
For a quick rundown of the available startup key combinations, see this post.
Old-school startup
Pressing the Power (⎋) key will boot your Mac normally. You can also press and hold this key after OS X has loaded to quickly restart, turn off or send your Mac to sleep. Another tip: pressing it briefly to shut down only your Mac’s display.
If your Mac is set to boot from a non-OS X volume, like a Windows partition, pressing X at boot time will start it up from your designated OS X startup volume.
Start it up from a bootable CD/DVD
If your Mac has a built-in optical drive and you have a bootable media at hand, you can start up the computer right from it. This is useful when your Mac’s startup drive breaks beyond repair or you want to reinstall the operating system using the OS X installer CD/DVD media, if one came with your computer.
Insert a CD/DVD into the drive, then turn on or restart your Mac and hold the C key immediately upon hearing the startup chime. To open the disc tray, simply press the left mouse button on a wired mouse at boot time.
RELATED: Startup up your Mac from CD/DVD drive
Choose your startup device at boot time
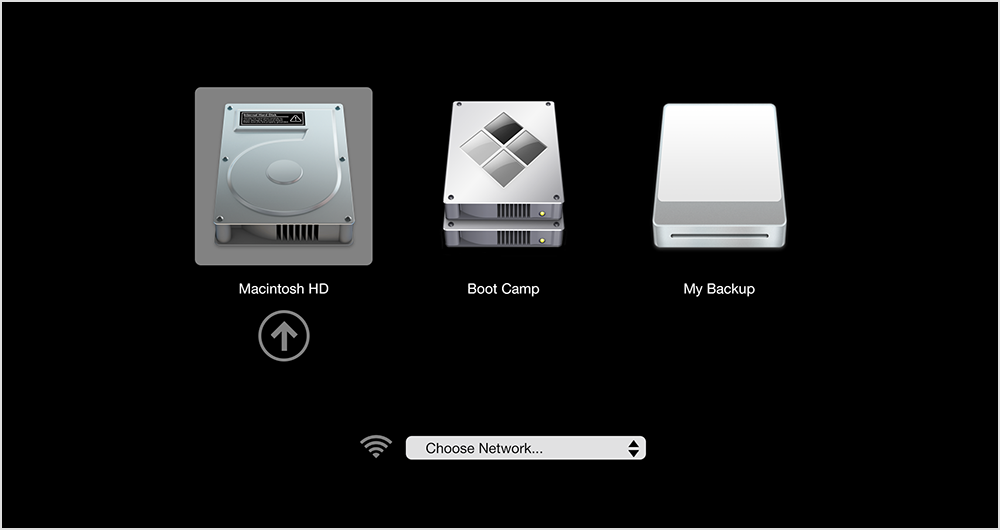
Using OS X’s built-in Startup Manager, you can pick a disk to startup your Mac from at boot time. Simply press and hold the Option (⌥) key immediately upon hearing the startup chime to invoke Startup Manager.
After scanning your connected drives and volumes for bootable copies of OS X, Widows, Linux or another operating system, Startup Manager displays your options. Highlight a volume and hit Enter to boot the computer from the selected volume. To open the optical drive when choosing a startup disk, press Command (⌘)-Period (.).
RELATED: Using Startup Manager to select your startup disk at boot time
Start up in single-user mode
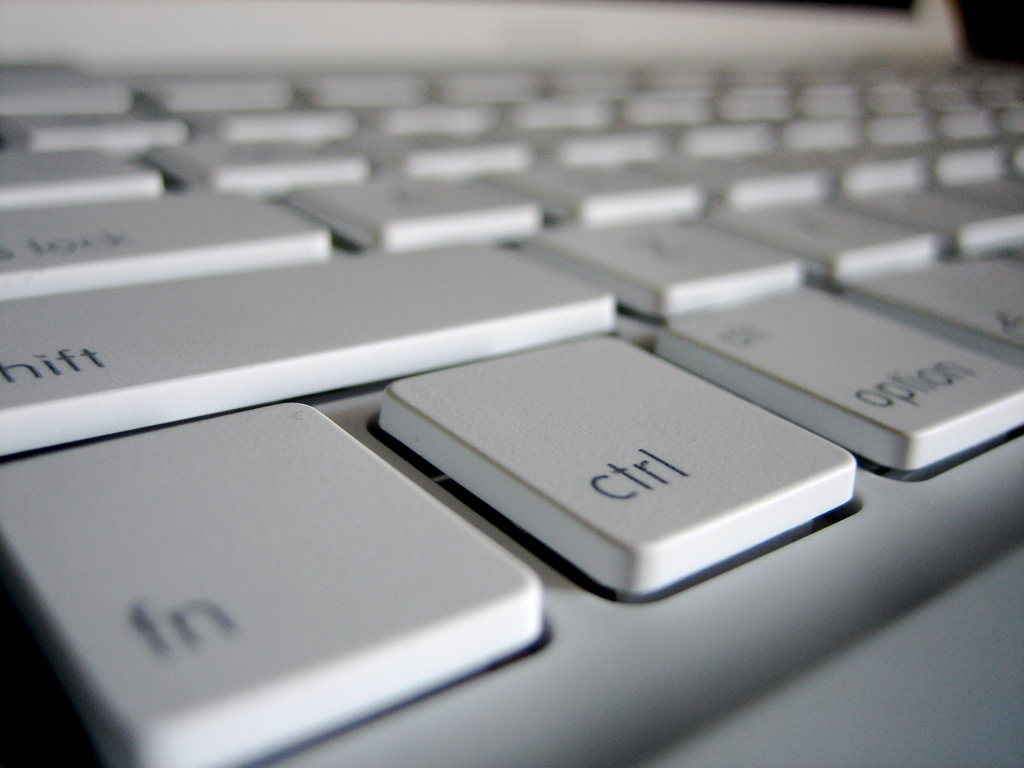
Pressing Command (⌘)-S after the startup tone loads OS X’s single-user mode, which can help you isolate issues related to startup. To exit single-user mode type “reboot” and press Enter.
When in single-user mode, the keyboard layout is US English.
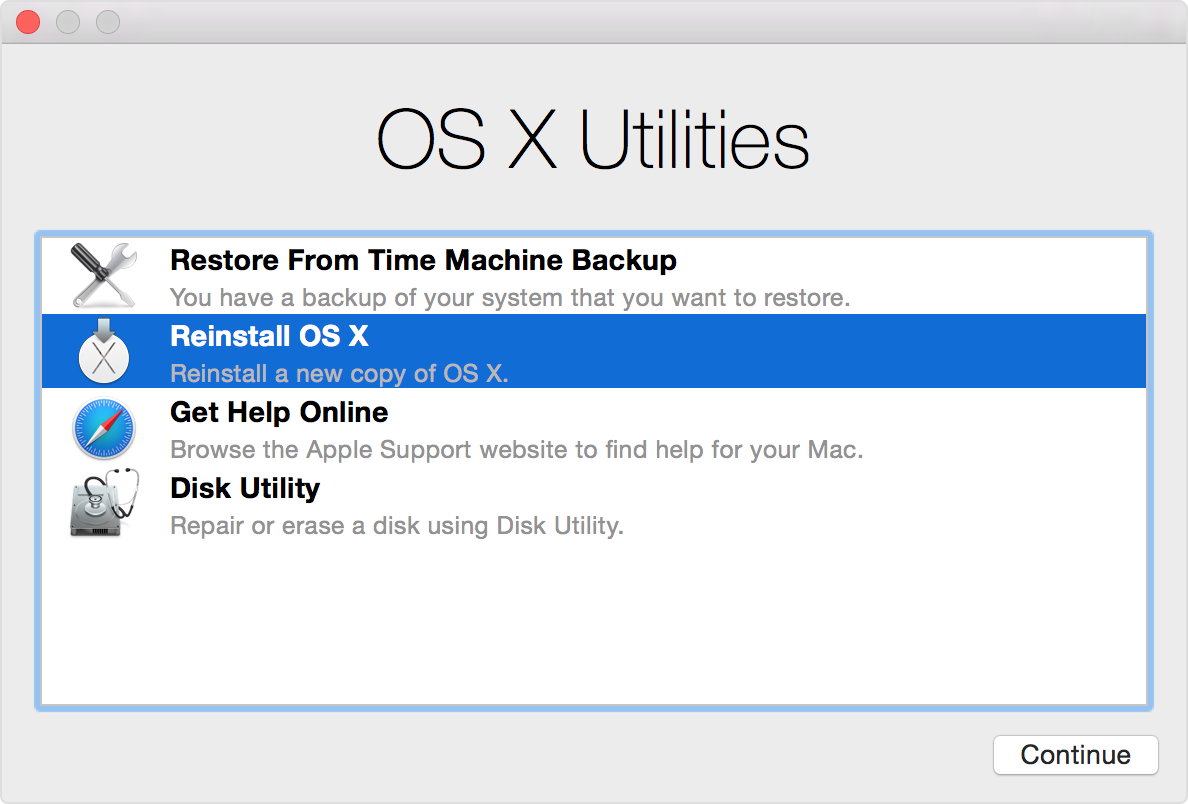
Troubleshoot your Mac in Recovery Mode
When your Mac starts acting up, OS X’s Recovery OS gives you the tools to troubleshoot the computer, repair disk errors, reinstall OS X, set a firmware password, restore the machine from a Time Machine backup and more.
These tools are kept on a recovery system image which itself resides on a hidden recovery partition located on your startup disk. To enter Recovery Mode, press Command (⌘)–R after the startup chime plays.
RELATED: Troubleshoot your Mac with Recovery OS
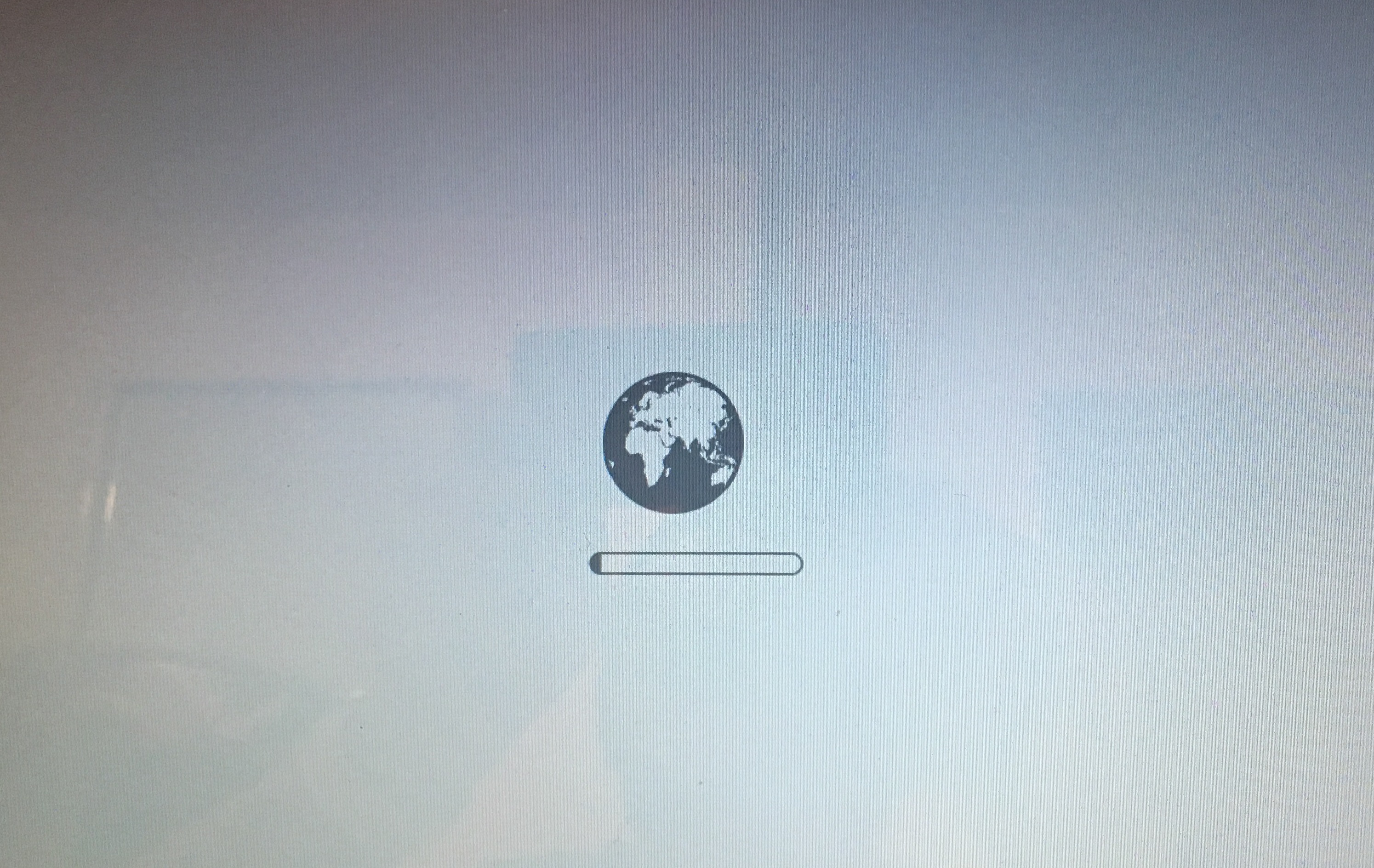
Recovery Mode broken? Boot OS X from Apple’s servers
If the recovery partition itself is damaged and you cannot enter Recovery Mode to troubleshoot your Mac, Internet Recovery Mode will help bring back the machine to working order. It downloads a recovery system image from Apple’s servers and then starts up your Mac from it.
RELATED: How to use Internet Recovery Mode
Like the regular Recovery Mode, Internet Recovery lets you repair disk errors, access the command line tools, restore from a Time Machine backup and more.
Using Internet Recovery, you can also download the version of OS X that originally came with your Mac. To enter Internet Recovery Mode, press Command (⌘)–Option (⌥)–R after the startup chime plays and hold the keys until the animated globe appears on the screen.
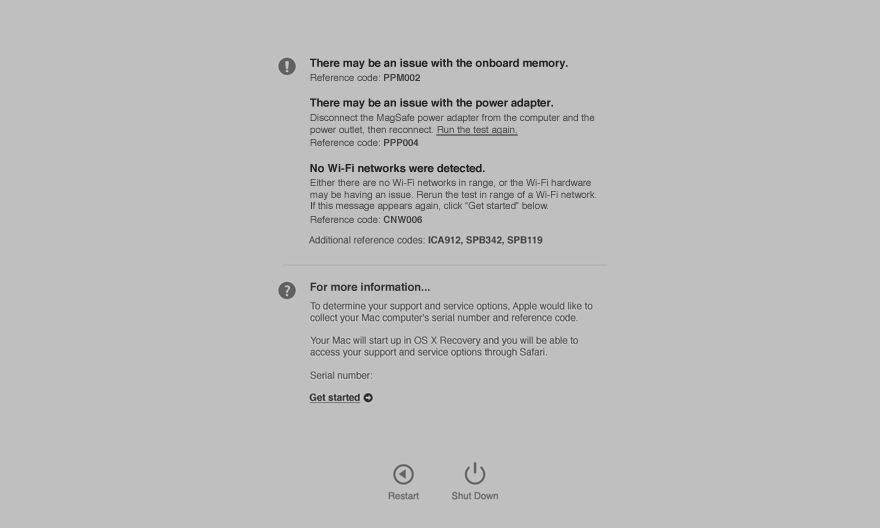
Pinpoint hardware woes with OS X diagnostics modes
If Recovery Mode or its Internet-based counterpart are unavailable or couldn’t fix system errors, enter OS X’s hardware diagnostics mode. Macs introduced before June 2013 include a diagnostics mode called Apple Hardware Test, which is an older version of Apple Diagnostics mode found on Macs introduced after June 2013.
These diagnostic modes run a barrage of tests to determine the overall health of your Mac and identify any potential underlying issues with its hardware. To start up to either Apple Hardware Test or Apple Diagnostics, press D or Option (⌥)–D after the startup chime, depending on which Mac you’re using.
RELATED: How to use Apple Hardware Test or Apple Diagnostics
In case your startup volume lacks these diagnostics modes, you can enter their Internet-based counterparts by pressing the Option (⌥)–D combination.
Isolate the cause of a software issue in Safe Mode
To determine the cause of a software issue on your Mac, use the Safe Mode which forces a directory check of your startup disk and then loads only required kernel extensions, essential OS X software and drivers. Startup and Login items and user-installed fonts are not loaded in Safe Mode.
The words “Safe Boot” appear in red letters in your Mac’s menu bar when you’re in Safe Mode. Your Mac runs slower than usual in Safe Mode because the bare minimum level of drivers, meaning no hardware-accelerated graphics for you in Safe Mode.
RELATED: How to use OS X’s Safe Mode
Due to only essential services being loaded in Safe Mode, certain OS X features and apps might not work correctly, including File Sharing. To enter Safe Mode, hold the Shift (⇧) key immediately after hearing the startup tone.
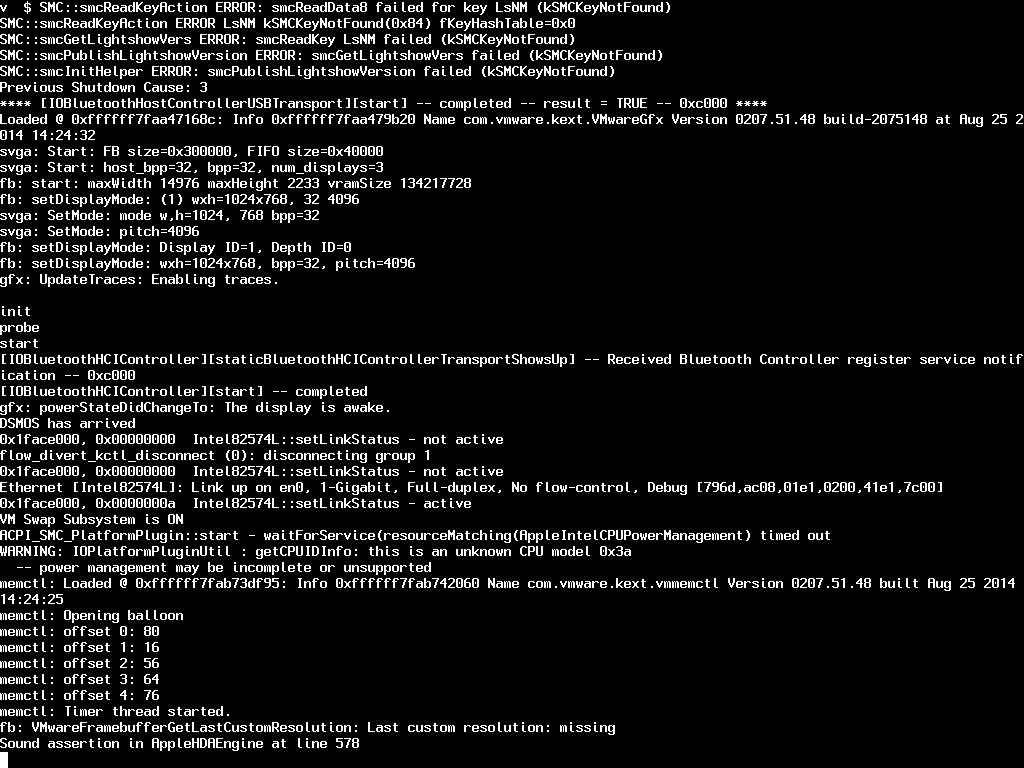
See what’s going on behind the scenes in Verbose Mode
Did you ever wonder what goes on behind the scenes as your Mac boots? With OS X’s Safe mode, you can! Simply Hold the Command (⌘)–V combination after hearing the startup chine to enter so-called Verbose Mode.
A text-only mode reminiscent of MS-DOS’s company line mode from the 1980’s appears, allowing you to observe as OS X loads one required component after another, from kernel extensions and drivers to other items. If any component fails loading, you should see an error message.
RELATED: Using command line-style Verbose Mode to start up your Mac
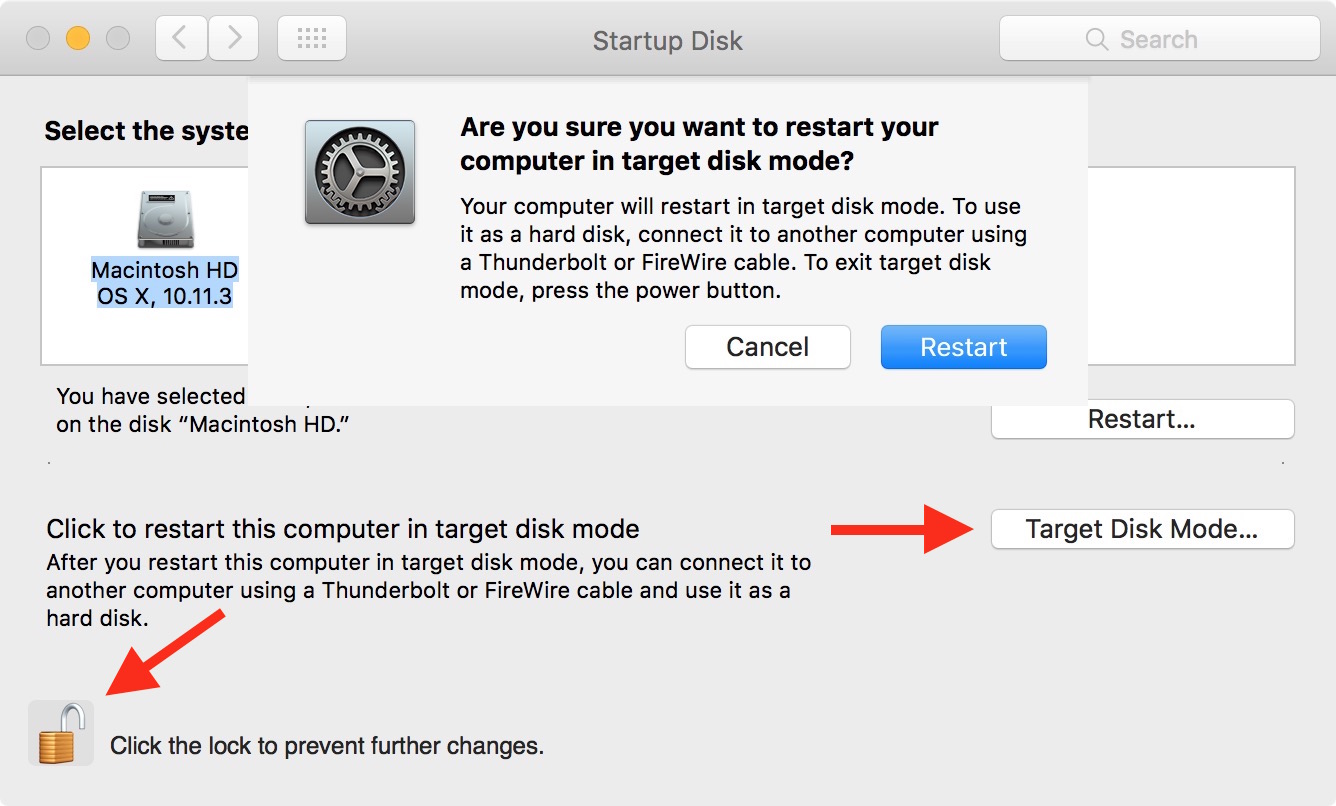
Browse other Mac’s drive in Target Disk Mode
Want to copy files from one Mac to another over an ultra-fast wired connection, but don’t want to fiddle with any network settings? No problem, just turn on the computer and hold the T key after hearing the startup chime.
Now connect that computer to another Mac, which must be booted regularly, with a Thunderbolt or FireWire cable. Just like that, its startup disk should appear on your Mac’s desktop, allowing you to copy files to and from it and more.
Don’t forget to eject the disk when you’re done using it.
RELATED: How to use OS X’s Target Disk Mode
Target Disk Mode can be invoked after OS X has loaded by going to System Preferences → Startup Disk, then click the Target Disk Mode button.
Boot from NetBoot server
You Mac can boot or reinstall OS X from a network.
Just hold the N key as the computer starts up, or select the NetBoot server using the Startup Disk preference pane or Startup Manager (hold down the Option (⌥) key while starting up).
To start up from a NetBoot server using the default boot image, press Option (⌥)-N at boot time. In order for NetBoot to work, another computer running OS X Server and the OS X Installer disk image must be on the same network as your Mac.
Reset PRAM/NVRAM
NVRAM is a non-volatile memory in your Mac that stores some essential configuration information, including the current display resolution, volume level, your default startup disk, time zone and so forth. Resetting NVRAM is often one of the last troubleshooting steps to perform before taking your computer to Apple.
RELATED: How to reset a Mac’s PRAM
To reset it, press and hold simultaneously the Command (⌘)—Option (⌥)—P—R combination when the startup chime play. Continue holding these keys until you hear the startup sound for a second time, then release the keys all at the same time.
Reset SMC
The System Management Controller, or SMC, manages certain hardware aspects of your computer, like fan speed, system backlight, indicator lights, power, port illumination and display management. If some of these features stop working properly, you should probably reset your Mac’s SMC.
RELATED: How to reset a Mac’s SMC
To do so, shut down your Mac first.
Next, hold the left-side Shift (⇧)—Control (⌃)—Option (⌥) keys along with the Power (⎋) button, all at the same time, until the computer turns on. Release the keys and then turn the machine back on using the power button.
Bypass your Login Items
If any apps, windows, servers or connected volumes are added in System Preferences → Users & Groups → Login Items , OS X will load them automatically as part of its normal startup process.
RELATED: Preventing OS X’s Login Items from leading when you log in
You can temporarily prevent Login Items and previously opened Finder windows from launching when you start up your Mac: hold the Shift (⇧) key after clicking the Log In button on the login screen and release it when the desktop appears.
Prevent automatic login
If the option to automatically log into OS X every time a Mac starts up is enabled in System Preferences → Users & Groups → Login Options, and you want to override it at boot time, hold the left Shift (⇧) key after the startup progress indicator shows up.
Startup key combinations not registering?
On certain Mac notebooks, these useful startup key combinations might fail to register.
12-inch MacBook owners, for instance, might complain about Apple’s wireless keyboard failing to pick up these keystrokes at startup. If you’re plagued with this issue regularly, simply use your notebook’s built-in keyboard or connect a wired keyboard.
Troubleshooting starts with the startup chime
You shouldn’t turn the volume all the way down when restarting your Mac because hearing different startup tones is another valuable troubleshooting hint which can help determine the cause of your issue.
RELATED: The different Mac OS X startup tones and the problems they indicate
For more tips like this, browse our complete tutorials archive.
Need help? Ask iDB!
Got stuck? Not sure how to do certain things on your Apple device? Let us know at help@iDownloadBlog.com and a future tutorial might provide a solution.
Shoot us your how-to suggestions at tips@iDownloadBlog.com.