In the refreshed iOS Security Guide, Apple has for the first time detailed security technologies pertaining to the Apple Watch.
As it turns out, the wrist-worn device borrows the many security features and technology built for iOS, including hardware-encrypted storage and data protection, keychain access control, protection of wireless data exchange with its paired iPhone and much more.
Here’s what you need to know about your Apple Watch and the security technologies it employs. Due to the highly technical nature of this topic, we have distilled key points into a human-readable format because not everyone is a security expert.
How Apple Watch keeps your data safe
Apple Watch uses the security features and technology built for iOS to help protect data on the device. Specifically, Apple has implemented hardware-encrypted storage and class-based protection of files and keychain items stored on your Apple Watch.
Access-controlled key bags for keychain items are also used.
And if you set up a passcode for your Apple Watch — and there a few reasons why you should do that — it will be entangled with the Apple Watch UID (Unique Device Identifier) to create encryption keys, providing an additional layer of security.
How Apple Watch secures the pairing process
For starters, you can only pair your Apple Watch with one iPhone at a time. Pairing the device with a new iPhone automatically erases all content and data on it.
This is by design.
For instance, should someone steal your Apple Watch (remember, Apple hasn’t implemented Activation Lock and Find My Watch features yet), they won’t be able to access your data because pairing your device to their iPhone will immediately wipe all the data clean.
Have you noticed an animated pattern resembling a particle cloud effect?
It appears on your Apple Watch screen during the pairing process and must be captured with your iPhone’s camera in order to pair the devices.
That, too, is not a pure gimmick.
This pattern contains an encoded secret that’s used for pairing over Bluetooth 4.1 (as a fallback pairing method, standard Bluetooth Passkey Entry is used).
Interestingly enough, Apple was recently awarded a patent for this unique pairing procedure, indicating the feature may come to other devices down the line.
Titled “Invisible optical label for transmitting information between computing devices” and depicted on the patent drawing below, the invention describes a method for encoding and decoding data-rich optical labels used to transmit small chunks of authentication data from one electronic device to another, much like QR codes.
In addition, the company is using an out-of-band pairing process which taps the NFC chip inside your Apple Watch to help exchange some information used in the pairing process, although pairing is completed using the Bluetooth radio.
Once the devices have been paired, the device will exchange public keys, followed by the Bluetooth link shared secret. This uses a process adapted from Apple’s iMessage, which uses Identity Service (IDS).
IDS is a directory of iMessage public keys, APNs addresses, as well as phone numbers and email addresses that are used to look up the keys and device addresses.
However, in this case Apple’s IDS servers are bypassed because the companion Apple Watch app on your iPhone already provides these services.
How Apple Watch secures communications with its paired iPhone
Once encryption keys have been exchanged during the pairing process, all wireless communications between the device is encrypted using IDS, with the encrypted Bluetooth and Wi-Fi links providing a secondary encryption layer.
The Apple Watch uses the rolling key encryption feature to change the encryption keys at 15-minute intervals to limit the exposure window, should traffic be compromised.
Finally, encryption keys used for communication between the Apple Watch and your iPhone are also secured using class-based protection.
How Apple Watch secures communications with the Internet
When the Apple Watch is outside the Bluetooth range of its connected iPhone, iCloud is used as a relay between the devices. Although the Apple Watch has built-in Wi-Fi, it won’t automatically join public wireless networks.
In fact, it will only join Wi-Fi networks that you previously joined on your iPhone. This ensures that the Wi-Fi credentials don’t have to be kept on the Apple Watch because your iPhone provides the list of known networks to the Apple Watch automatically.
How Apple Watch secures Siri
When Siri is used from you Apple Watch, the device creates its own random unique identifier. Siri requests initiated from the Apple Watch won’t re-send your information again to Apple’s servers. Instead, the Siri identifier of the paired iPhone is sent, which provides a reference to that information that’s already present on Apple’s servers.
How Apple Watch secures your apps
Currently, third-party applications for the Apple Watch run as WatchKit extension on your iPhone, with only user interface assets and a storyboard being sent wirelessly back to the Apple Watch.
This data is being encrypted as well.
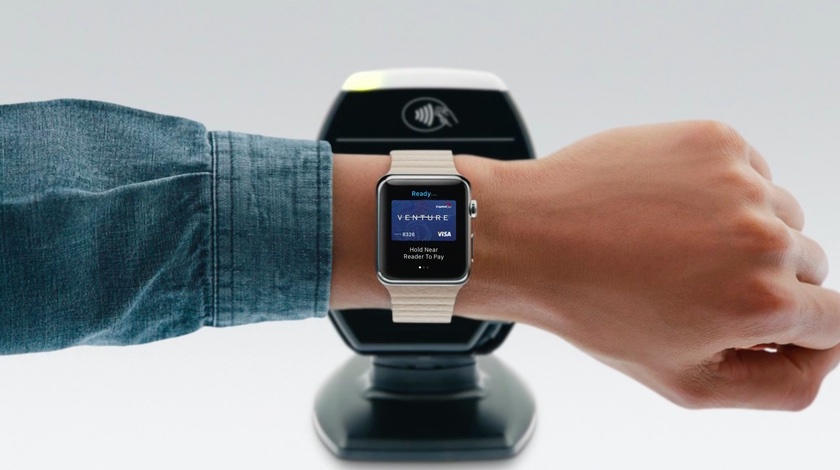
In addition, developers can specify that their apps only use local communication between the devices, bypassing iCloud. This is how Apple Pay works, as paying from your wrist is possible without the paired iPhone, or network connection for that matter.
To support apps that need streaming data, encryption is provided using methods similar to FaceTime encryption, utilizing the IDS service provided by the paired iPhone.
How Apple Watch secures Apple Pay
As mentioned before, developers can specify that their apps only use local communication between the devices, bypassing iCloud. This lets Apple Pay work without a network connection.
When the Apple Watch is unlocked and you have double-clicked the side button, the action gets detected and passed directly to the Secure Element of the NFC chip, without going through the S1 application processor.
This ensures that payment tokens are exchanged directly between a receiving NFC terminal and the NFC chip inside your Apple Watch. Tokens and data stored in the Secure Element are encrypted and physically isolated from the rest of the system, including the main processor and apps.
As the gateway to the Secure Element, the NFC controller ensures that only payment requests arriving from an in-field terminal are marked as contactless transactions.
Once payment is authorized on an unlocked Apple Watch by double-clicking the side button, contactless responses prepared by the payment applets within the Secure Element are exclusively routed by the controller to the NFC field.
“Consequently, payment authorization details for contactless transactions are contained to the local NFC field and are never exposed to the application processor,” Apple says.
When your Apple Watch is locked, Apple Pay can’t be used.
In fact, credit cards added to the Secure Element within the Apple Watch are marked as invalid when the device’s passcode is disabled, your Apple Watch is unpaired from its iPhone or Wrist Detection is turned off.
And if you disable the automatic locking option provided by the Wrist Detection feature, Apple Pay will be immediately disabled for security purposes.
Apple Watch and Wrist Detection
The Wrist Detection is an important security feature of the Apple Watch. It uses skin contact to detect that your Apple Watch is being worn and locks the device automatically when you’re not wearing it.
For security purposes, disabling Wrist Detection also disables Apple Pay.
Wrist Detection is turned off using the Apple Watch companion app on your iPhone (My Watch > General > Wrist Detection), but can also be enforced using mobile device management.
Locking and unlocking Apple Watch
Apple provides a quick way to manually lock your Apple Watch by pressing and holding the side button until the sliders appear. Then drag the Lock Device slider to the right and you’ll be required to enter your passcode the next time you try to use your Apple Watch.
The paired iPhone can also unlock your Apple Watch, provided the watch is being worn and the Wrist Detection feature has been enabled. Apple even employs motion heuristics to attempt to automatically lock the device shortly after it’s removed from the wrist.
Again, for security purposes Apple Pay can’t be used when your Apple Watch is locked. And should the automatic locking option provided by Wrist Detection be disabled in settings, Apple Pay will be turned off as well.
If you’ve told your Apple Watch to unlock automatically when its paired iPhone is unlocked using the Apple Watch companion app, the two devices establish a connection authenticated by the encryption keys established during the pairing process.
Your iPhone first sends the key, which the Apple Watch uses to unlock its data protection keys. Apple claims that your Apple Watch passcode is not known to the iPhone, nor is it transmitted, so it can’t be harvested from a stolen phone.
As an additional security pre-requisite, this feature is unavailable when you set up a complex passcode on your Apple Watch, meaning you must punch in your passcode manually.
You now hopefully have a much clearer picture of the lengths Apple’s engineers have gone to in order to build a very secure, tiny computer for your wrist.
iOS is routinely applauded for its strong security and borrowing its many data protection and security features for the Apple Watch is definitely a smart move on Apple’s part.
Thoughts?
Grab the iOS Security Guide as a free PDF download from Apple.
Hat tip goes out to Twitter user @marcinw for bringing the updated iOS Security Guide to our attention.